Axons of the Corticospinal Tract Cross the Brainstem at the
There are two divisions of the corticospinal tract the lateral corticospinal tract and the anterior corticospinal tract. B the lateral corticospinal tract includes neurons from the premotor cortex.

Organization Of The Human Corticospinal Tract Mn Groups Vulnerable Download Scientific Diagram
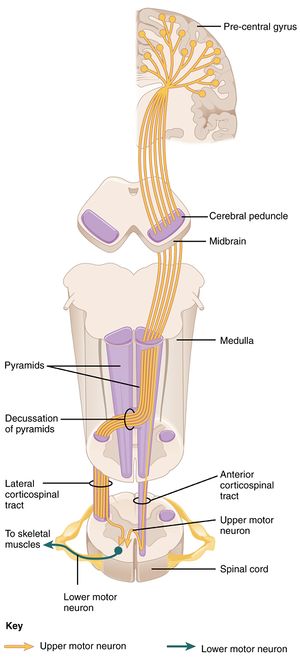
In the medulla corticospinal fibers continue caudally and in the most caudal portion of the medulla approximately 90 percent of them cross over to the other side.

. The corticospinal tract AKA the pyramidal tract is the major neuronal pathway providing voluntary motor function. As you should now know the medullary pyramids are two prominent columns of white matter along the ventral midline of the medulla. Multiple Choice posterior preganglionic postganglionic terminal primary Axons of the corticospinal tract cross the brainstem at the Multiple Choice middle cerebellar peduncle of the pons.
It is composed of four sections in descending order. The diencephalon midbrain pons and medulla oblongata. Likewise where does the Corticobulbar tract originate.
Cerebral aqueduct of the midbrain. The corticospinal fibers continue caudally and in the most caudal region of the medulla about 90 of them cross to the opposite side. The corticobulbar axons leave the tract as it descends in the brainstem and terminate in the motor nuclei of the various cranial nerves.
These axons tend to make contact with motoneurones innervating the axial muscles. Raphe nuclei axons to brain stem and spinal cord. The lateral tract forms about 90 of connections in the corticospinal tract.
A majority of the axons cross the midline at the pyramidal decussation between the brainstem and spinal cord to form the lateral corticospinal tract Figure 1A. Decussation of the pyramids in the medulla. The lateral corticospinal axons terminate at all spinal cord levels primarily on interneurons but also on motor.
This crossover causes the left side of the brain to control the right side of the spinal cord and the right side of the brain to control the left side of the spinal cord. Reorganization of the pattern of CST projections to the spinal cord during evolution led to improved motor skills. The targeting of primary CST axons to the spinal cord is followed by axon collateral branching to several target areas and then by pruning of specific collateral branches 7 9.
The vast majority cross over in the medulla while the. The corticospinal fibers continue caudally and in the most caudal region of the medulla. What attenuates pain sensation and what is release in that process.
Next select a key component of the corticospinal tract such as the medullary pyramids in the section identified in the navigation window as 8-medulla. The corticospinal tract is a network of nerve cells axons that transports data about motion from the brain areas around the cerebral cortex to the spinal cord. In particular most CST axons cross the anatomical midline at the junction between the brainstem and spinal cord forming the pyramidal decussation.
As the corticospinal tract travels down the brain stem a majority of its fibers decussate to the contralateral side within the medulla then. Axons of corticospinal tract crosses the midline X shaped region in anterior aspect of medulla anterior horns at medulla consist basically of what accessory nucleus for cranial nerve XI. The corticobulbar tract originates in the.
Besides where does the corticospinal tract terminate. At the bottom of the pyramids there is a pyramidal decussation which is the point where 90 of the axons cross over to the opposite side of the brainstem and form the lateral corticospinal tract. On either side of it there are two bumps called the pyramids which contain axons of the corticospinal or pyramidal tract.
Axons from the corticobulbar tract emerge as it descends in the brainstem and go to the motor nuclei of the numerous cranial nerves where they terminate. The lateral corticospinal tract neurons cross the midline at the level of the medulla oblongata and controls the limbs and digits. A the lateral corticospinal tract consists of axons that project from the motor cortex to neurons in the brainstem and remain ipsilateral descending into the spinal cord.
Ponsdorsal raphi nucleus and raphi nulei axons to thalmus limibi sys and most of the cerebral cortex. This tract connects the cortex to the spinal cord to enable movement of the distal extremities1. What are the serotonergic neurons and nuclei in the brainstem and their projections.
In the brainstem they are guided along the pyramidal tract and turn dorsally at the pyramidal decussation to cross the midline and reach the contralateral side of the spinal cord Figure 1a. Before entering the spinal cord these fibers cross over to the opposite side forming the decussation of the pyramids. A minor proportion 10 of corticospinal tract axons do not cross the midline in the decussation of the pyramids but continue to travel caudally in the anterior columns before crossing over to the opposite ventral horn at a segmental level.
The corticospinal tract is a white matter motor pathway starting at the cerebral cortex that terminates on lower motor neurons and interneurons in the spinal cord controlling movements of the limbs and trunk. Lateral to each pyramid there are two oval bumps called the olives. In an autonomic motor pathway the first cell in the two-neuron chain is the neuron.
It is responsible for many vital functions of life such as breathing consciousness blood pressure heart rate and sleep. The brainstem is the structure that connects the cerebrum of the brain to the spinal cord and cerebellum. The corticospinal and corticobulbar pathways are illustrated in Figures 1 and 2.
Neurons in layer V of the motor cortex give rise to axons that descend through the internal capsule the cerebral peduncle and the medullary pyramids to the caudal end of the medulla where most of them cross in the pyramidal decussation. The nerve cells of the corticospinal tract arise from cortical regions while moving downwards towards the brainstem and then into the spinal cord. C the two reticulospinal tracts control automatic locomotion and posture movements.
They then descend in the contralateral lateral funiculus as the lateral corticospinal tract. To begin open Sylvius4 enter the Brainstem Cross Sectional Atlas and select All structures.
Corticospinal Tract Physiopedia

Organization Of The Human Corticospinal Tract Mn Groups Vulnerable Download Scientific Diagram
Comments
Post a Comment